In-depth Cardiovascular Definition, What You Need to Know
At the center of cardiovascular definition is the heart, blood and blood vessels. However, these components do not exist in a vacuum. They are critical to the entire circulatory system of human biology. The circulatory system is also refereed to as the cardiovascular system.

By combining the word system with cardiovascular, we effectively imply correlated function of the main cardiovascular elements, that is, the heart, blood and blood vessels. The cardiovascular system is therefore primarily made up of the heart, blood and the expansive network of blood vessels.
Furthermore, blood vessels in the cardiovascular system have their respective names and types and are not all the same nor do they serve the exact same purpose. However, they have a singular goal which is to perpetuate a system of life.
As may have already been noticed, while at first cardiovascular definition may sound simple, once the definition takes into account the system part, the cardiovascular system becomes a complex and intelligent system that is capable of regulating itself so as to work in perfect harmony and balance.
If we relaxed the rules, cardiovascular definition would simply be allowed in short to mean human life and here is why...
Cardiovascular Definition, The Workings of the Cardiovascular System
One of the critical elements to highlight when defining the cardiovascular system is that each of the components in the system is dependent on each other and in the process sustains life. If one component is compromised it has implications for the other components in the system sometimes with dire consequences.
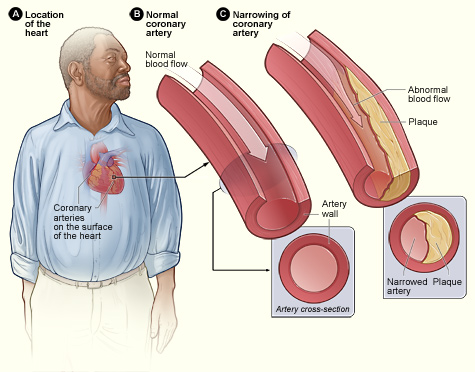
For example, stiff blood vessels will cause high blood pressure or hypertension. In turn, uncontrolled hypertension results in organ damage. There is a high risk of the damaged organ being the heart which in turn results in heart disease. On the other hand, heart disease that is not related to high blood pressure may result in secondary hypertension, for example. The dependence is not only critical but extraordinarily complex.

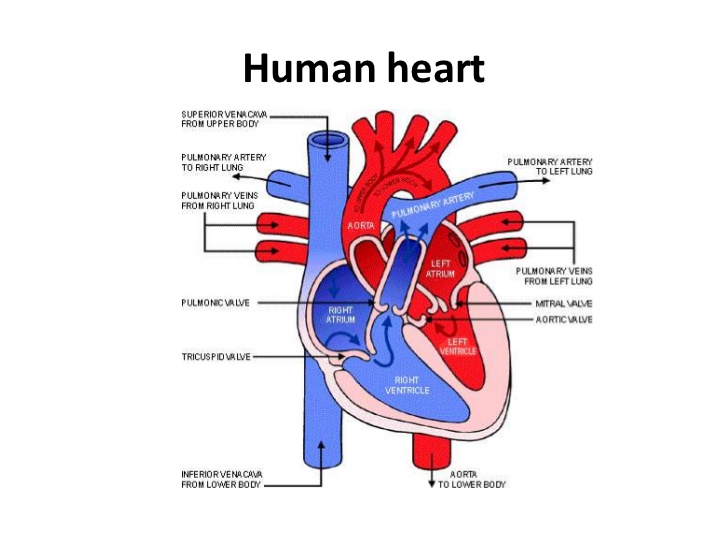
In our continuing examination of cardiovascular definition to the fullest extent, we inevitably must consider the purpose of the cardiovascular system. The cardiovascular system is a blood circulatory system. This is to say, the components that we identified in our cardiovascular definition depend on the blood to deliver nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body.
What this means is that the blood circulatory system is essential in keeping the cells alive and functioning. While one side of the function of the cardiovascular system is to transport life giving nutrients and oxygen to all parts of the body, the other half of the story is that the blood circulatory system is also an efficient waste disposal system.
Oxygen Rich Blood Vs Oxygen Poor Blood
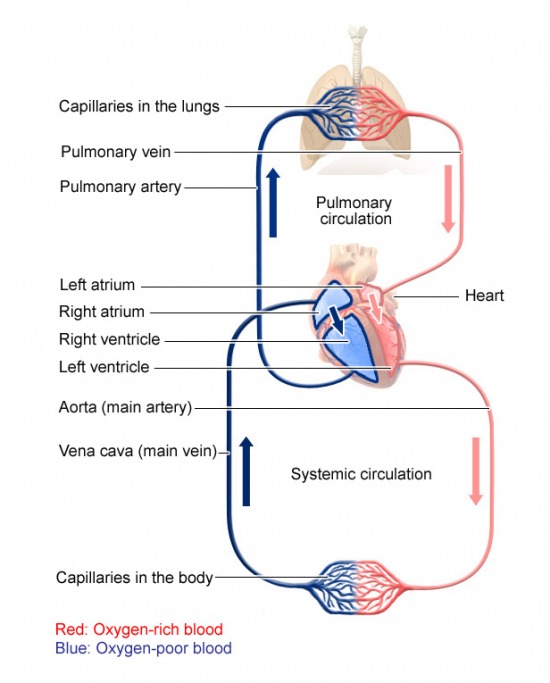
The way the cardiovascular system works is that oxygen rich blood leaving the lungs travels to the heart where it's pumped under a normal blood pressure reading of no more than 120 over 80 mm Hg and no less than 140 over 90 mm Hg (120/80-140/90).
The oxygen rich blood is pumped out of the heart to the rest of the body laden with oxygen and nutrients. It reaches the utter most ends of the body's cells using a system of capillaries. Capillaries are a fine network of blood vessels that reaches the tissues and body organs.
After dumping oxygen and nutrients, using the vena cava or main vein, blood returns from the cells found in body tissue and organs laden with carbon dioxide and other waste. At this point, it is the so called oxygen poor blood. Using the pulmonary vein, oxygen poor blood expels the carbon dioxide on return to the lungs and toxic waste through the kidneys.
By definition, the cardiovascular system does these runs on a non-stop basis to keep the cells alive and by extension the body alive. Each heartbeat marks the beginning of a new cycle of this systematic circulation. The heart beats some 70 times per minute when rested.
Cardiovascular Disease Definition
Cardiovascular disease definition is made easier to appreciate keeping in mind the foregoing cardiovascular definition which must necessary encompass the cardiovascular system as already highlighted.
In an editorial published in the journal Circulation in 2006, the writers lamented the situation medicine finds itself when it comes to definitions as follows;-
Medicine has struggled through its long history to define accurately the various diseases that are a daily component of the human condition
This is also true for cardiovascular disease definition. In fact, in the quote above, the scientists were lamenting the fragmented definition of heart attack also known as myocardial infarction (MI).
Whereas the definition of cardiovascular disease must encompass a wide range of diseases pertaining to the heart and blood vessels, often times a good deal of medical information has gone on to narrowly express the range of cardiovascular disease.
The reasons are understandable and mostly emanate from the fact that certain cardiovascular diseases have been dominant more than others and therefore written and talked about more. This has given the impression that the limited focus on certain diseases in themselves complete the definition of cardiovascular diseases.
In reality, as mentioned, a well considered cardiovascular disease definition encompasses an extensive cluster of diseases that occur in relation to the heart and blood vessels.
Image Credit: Science Picture Co
According to Omid Hajiseyed Javadi, MD, a thoracic surgeon at Good Samaritan Hospital located in Silicon Valley, the United States:-
Cardiovascular disease is a range of problems that occurs to the heart and blood vessels that are either supplying the heart or the blood vessels that are supplying the body. The range of problems encompass valvular disease as well as arterial disease. The valvular disease can be congenital, the arterial disease type processes can be from acquired problems such as having high cholesterol, sugars that are out of control and smoking. It is a large encompassing set of problems that can occur.
By the same token, the following is a range of diseases and disorders, some of which are hardly mentioned in everyday life, falling into the definition of cardiovascular disease.
|
Myocardial infarction Hypertension Irregular heartbeat Aneurysms (artery enlargement) Stroke Heart valve disease Metabolic syndrome Cardiomegaly (enlarged heart) Valvular heart disease Endocarditis (infection of inner lining of heart chamber and valves) |
Coronary heart disease Angina (chest pain) Inherited heart disease Peripheral vascular disease Cardiac arrest Embolism (vessel blockage) Syncope (fainting) Venous thrombosis (blood clot) Congenital heart disease Mitral insufficiency (improper closing of valve when heart pumps) |
Cardiovascular Endurance Definition
Cardiovascular endurance definition is the body's ability to conduct large-muscle, whole-body exercise at moderate to high intensities over an extended period of time before fatigue sets in
This continued performance at high intensity is also refereed to as exertion.
Cardiovascular endurance is alternatively called cardio-respiratory endurance, aerobic fitness or aerobic capacity. All these synonyms have one thing in common which is that oxygen is involved to sustain the activity. As such, cardiovascular endurance necessarily relates to cardiovascular exercise.
Even so, cardiovascular endurance is associated with specific types of exercises and aerobic exercising equipment that depend on cardio-respiratory endurance for any meaningful cardiovascular benefit. Good examples of such activities is swimming and cycling.

In many ways, cardiovascular endurance defines outcomes in sporting competitions. In this regard, a 2017 review in the journal Nutrients (2017 Jan; 9(1): 43) highlighted the benefits of beetroot supplementation in increasing cardiovascular endurance particularly in athletes. It is not surprising then that aerobic capacity is therefore a highly sort after resource among many types of athletes.
In discussing cardiovascular endurance definition, it is worthwhile pointing out that cardio-respiratory endurance depends on the body's ability to sustain skeletal muscle activity during intense aerobic metabolism.
Also refereed to as aerobic respiration, aerobic metabolism occurs when oxygen is used to generate energy using sugars or carbohydrates found in the muscles. The energy that is produced is known as adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
To demonstrate the extent to which cardiovascular endurance is dependent on the cardiovascular system beyond just the supply of oxygen, we point out that as ATP is being generated also is waste which the circulatory system, as shown in the cardiovascular definition earlier, expels from the body.

In other words, the production of ATP during aerobic metabolism is dependent on three key factors namely 1) delivery of oxygen from the outside environment to the working cells in the active muscles, 2) use of the oxygen once it has reached the muscles and lastly 3) the expulsion of the waste produced in the process.
Studies reveal that the condition of a person's heart, lungs, blood and blood vessels is directly linked to their ability to have a high level of cardiovascular endurance. This is important to keep at the back of the mind when discussing cardiovascular endurance definition.
As a matter of fact, before science got to the bottom of it, there was what was once refereed to as the athlete's heart associated with well trained high performing runners. It was believed to be an abnormal condition which has however since been accepted as actually representing a highly efficient organ.
Also to be considered as part of cardiovascular definition is how cardiovascular endurance is measured or tested.
VO2max is the symbol of maximal aerobic power. There are two ways to express maximal aerobic power which can be liters of oxygen consumed per minute (I/min) or milliliters of oxygen consumed per kilogram of body weight per minute (ml/kg/min). The latter facilitates endurance measurement of different body sizes.
Consequently, VO2max is useful to physicians as it could theoretically predict a person's risk of CVD including high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, certain types of cancer and even premature death from all causes.
According to a report published in the Journal of Physical Therapy Science ( 2016 Feb; 28(2): 641–645), a decline in cardiovascular endurance, "significantly increases the probability of lifestyle diseases and health impairments". In addition, the report concluded that cardiovascular endurance is a critical element of physical fitness.
The foregoing in-depth discussion of cardiovascular definition has revealed what lies beneath the inter-dependent function of the heart, blood and blood vessel components which are indispensable members of the cardiovascular system.
Also existing in the context of the cardiovascular system is cardiovascular endurance definition which we have also elaborated and proceeded to examine some of its important aspects and implications.
[Last updated: 12 November 2017]

|
Home > Hypertension |
Cardiovascular > Cardiovascular Definition |
Disclaimer
Information contained on this website is not meant to replace your doctor's advice.
(c) All Rights Reserved. 2010-2018