Vitamin C and Heart Disease, What You Need to Know
The correlation between Vitamin C and heart disease has been a subject
of scientific investigation for many years. In case you maybe doubtful,
rest assured that there is indeed a scientifically proven beneficial
relationship between the two as we shall show.
The story of
Vitamin C goes as far back as 1928 when this dietary antioxidant was
first isolated. Since that time, interest in Vitamin C has continued to
expand.

It is also of interest to mention here that while the popular name is Vitamin C, the other seldom used name in everyday language is ascorbic acid or simply AA. For this reason you shall find in this article this interchanging use of the name, let it not be a source of any confusion!
Researchers and practitioners have applied varying doses of Vitamin C to treat and even reverse a number of health problems including arterial blockage also known as atherosclerosis, cancer, common cold, fertility issues, diabetes, immunity problems, neurodegenerative disorders and heavy metal toxicity among other health related issues.
Quick Facts about Vitamin C
- The human body cannot synthesize Vitamin C
- Animals sources of Vitamin C are poor providing less than 40mg per 100g
- Plants are major sources of Vitamin C at 5000mg per 100g
- Vitamin C toxicity is very rare
- Dietary Vitamin C is absorbed by the small intestines
One of the benefits derived from the relationship between Vitamin C and heart disease is found in the role played by AA in treating atherosclerosis.
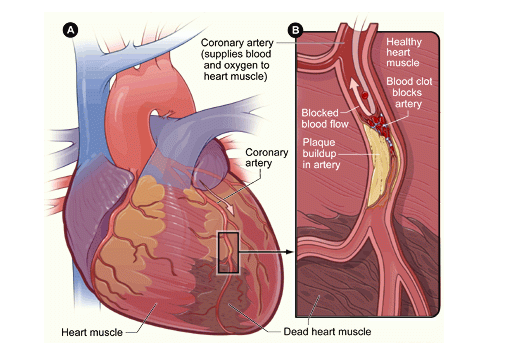
Atherosclerosis refers to the progressive build-up, often over decades in time, of fats and cholesterol along arterial walls with known health problems such as high blood pressure and coronary heart disease (CHD). We have previously written extensively on CHD as a major cardiovascular issue.
One of the well known paths to the development of heart disease is an overwhelming presence of bad cholesterol in the bloodstream. Vitamin C does something about it...
Vitamin C and Heart Disease: Vitamin C Prevents and Reduces Bad Cholesterol
During certain studies scientific investigators began to observe that the administration of Vitamin C was responsible for lowering bad cholesterol (LDL) and increasing good cholesterol (HDL). Furthermore, ascorbic acid also lowered triglycerides and other blood lipids.
These serum substances are responsible for the clogging up that occurs in arteries leading to coronary heart disease. The complications of CHD include heart failure, heart attack and stroke.
Not only did studies show that Vitamin C reversed high levels of cholesterol in the blood, it was also shown that Vitamin C deficiency led to increased bad cholesterol levels.
A 1988 study published in the journal Acta Biologica Hungurica (1988;39(1):49-57), confirmed the positive correlation between Vitamin C and heart disease noting that "chronic Vitamin C deficiency seems to affect the blood lipid profile unfavorably which could promote atherogenesis."
Atherogenesis refers to the process of plaque build-up in human artery walls which leads to heart disease.
A 1 % fall in blood cholesterol through a Vitamin C rich vegetarian diet can lower the risk of suffering a heart attack by at least 2 % - Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry
The Acta Biologica Hungurica study was conducted using animals in the form of guinea pigs whose AA intake was restricted to only 0.5mg/day compared to their counterparts which had 5mg/day in Vitamin C.
In another 1971 study published in the highly regarded science journal Lancet (1971 Dec 11;2(7737):1280-1), it was noted that in "healthy people under the age of 25, cholesterol levels tended to fall when 1 g of Vitamin C per day was added to an otherwise normal diet".
Considering that efficient and adequate Vitamin C supply comes from plant sources (see Quick Facts), Vitamin C deficiency which increases the risk of heart disease is in many ways a nutritional or dietary issue.
On the flip side of the coin is that heart disease care and treatment would inevitably encompass dietary modifications to include plants and leafy greens rich in Vitamin C. Other heart healthy dietary considerations which we have written about centre around fish and fish oil which must not be ignored in a wholesome persuit of a heart healthy diet.
Sources of Vitamin C
- Citrus fruits
- Green peppers
- Red Peppers
- Tomatoes
- Brussels sprouts
- Turnip
- other Leafy veggies
We now turn to consider the benefits of Vitamin C in dealing with atherosclerosis, a dreaded cause of heart disease.
Vitamin C and Heart Disease: Vitamin C Reverses Atherosclerosis
Apart from preventing and/or reversing the accumulation of bad cholesterol in the blood, there are bold claims that began emerging in the 1950s pointing to the power of Vitamin C to actually reverse atherosclerosis which is the dreaded build up of plaque in the arteries.
If the clogging that occurs in the arteries could be reversed as per these claims, then in a serious way heart disease or coronary artery disease, to be precise, would indeed be reversible.
Mainstream cardiovascular science does not exactly converge on this view. According to some opinions there is a reason for this which we shall highlight shortly.
In the meantime, the link between Vitamin C and heart disease in respect of the reversal of atherosclerosis appears to be a claim associated with the holistic healing community. This is a community which is well known for promoting natural non pharmaceutical therapies in addressing heart disease and other illnesses.
For instance, in an article entitled Reversing Heart Disease with a Vitamin published in the Well Being Journal of July/August 2011 (page 10), Daniel Cobb, an oriental medicine practitioner, put forward a strong view that Vitamin C is crucial in the reversal of artery plaque build-up.
According to Cobb, atherosclerosis should be viewed as the body's natural response to saving your life by preventing deadly breakthrough bleeding as a result of arterial damage.
Cobb writes:-
The plaque deposits that heart disease patients have been told to be so afraid of are actually band-aids purposely placed by the body at weak points of the arteries to prevent deadly breakthrough bleeding
The understanding here is that plaque build-up follows damage to arterial walls as a way of plugging the damaged area to prevent a potentially fatal outcome. Plaque build-up is, according to this understanding, plan B, as it were, adopted by the body when faced with Vitamin C deficiency.
Assuming that Vitamin C was in adequate supply, plaque would not necessarily build up to the point of causing coronary heart disease as we know it. Cobb maintains that the body would employ the available Vitamin C together with other nutrients to create new collagen and elastin fibers necessary for the repair of damaged artery walls.
It is from the belly of this notion that Cobb contends that simple abundant Vitamin C supplements or through their dietary sources taken on a regular basis are capable of reversing atherosclerosis or at least substantially regress artery clogging. This is the link between Vitamin C and heart disease according to this strongly held position.

To sum it all up, Daniel Cobb stands by the idea that Vitamin C reverses atherosclerosis thereby treating heart disease. He states that:-
Out of all my heart disease patients, I have had only one who did not improve significantly, and that one patient did not use the recommended type of vitamin C. Another patient last year completely reversed her heart disease in 2 months
It is worthwhile stating that Cobb is a highly regarded authority in the alternative and integrative medicine community and his views are therefore held in high regard by some.
Why hasn't the Vitamin C and Heart disease theory become mainstream?
According to oriental medicine practitioners, the curative link between Vitamin C and heart disease has not been advertised as such nor glowingly promoted because it threatens the position of big pharmaceutical corporations.
If the necessary supplements including Vitamin C that are needed to treat atherosclerosis can be available for as little as $90.00 (ninety dollars), as stated by Cobb, then any promotion of Vitamin C as a cure for atherosclerosis dooms big pharma as it is curtly known.
Furthermore, in addition to alleged downplaying of the benefits of Vitamin C in treating heart disease in some studies, it has also been noted that there have been very few controlled scientific studies investigating the claim.
As to whether one should look to Vitamin C for the reversal of coronary artery disease, the answer is that there appears to be overwhelming support of this theory.
Above all, perhaps the most important consideration is that there is little harm if at all in trying it out. Vitamin C at regular doses produces little to no side effects. At higher doses, there could be some discomfort such as diarrhea but overall is generally considered safe.
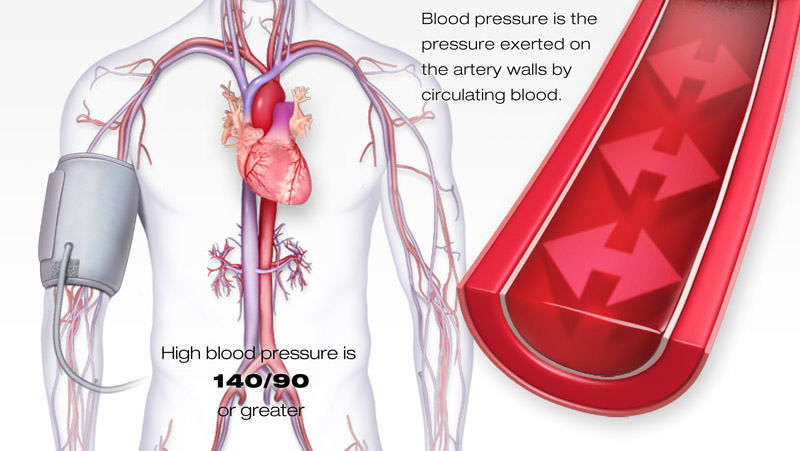
Vitamin C and Heart Disease: Vitamin C Lowers Blood Pressure
Even if Vitamin C failed to treat artery clogging there is one more thing that mainstream science acknowledges it can do - lowering blood pressure.
A well known risk factor of heart disease is hypertension. It follows that preventing, lowering and better managing high blood pressure is essential to the prevention and treatment of heart disease.
Some of the heart issues that follow high blood pressure include left ventricular hypertrophy which is essentially the excessive thickening of the heart muscle, heart failure and ischemic heart disease.
The science behind Vitamin C being effective in reducing blood pressure is embedded in the fact that antioxidants have a beneficial effect on the endothelium which is a thin lining of blood vessels. The endothelium plays a crucial role in regulating blood pressure. Vitamin C along with Vitamin E are well known antioxidants.
Here are what some studies have revealed...
The Journal of Human Hypertension Study
Back in 1997 writing in the Journal of Human Hypertension (1997 Jun;11(6):343-50) investigators shared that:-
We found a consistent cross-sectional association between higher vitamin C intake or status and lower BP...
Their findings, although leaving room for further research, confirmed observations that there is a protective link between Vitamin C and cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, this protective benefit is mediated by the effect Vitamin C has on blood pressure.
This study was premised on meta-analysis of data drawn from previous studies. Overall, the investigation revealed that Vitamin C intake or blood Vitamin C presence had an inverse relationship with blood pressure.
The Journal of Chiropractic Medicine Study
In 2006, a study published in the Journal of Chiropractic Medicine (2006 Summer; 5(2): 60–64) discovered that after 6 weeks of daily intake of 500mg of Vitamin C, both systolic blood pressure (top number) and diastolic blood pressure (bottom number) reduced.
According to the researchers, systolic blood pressure went down by some 3.9 mm Hg while diastolic blood pressure reduced by some 2.1 mm Hg.
Considering that slight changes in blood pressure represent significant cardiovascular event risk status, these reductions are very meaningful and welcome. Cardiovascular events refer to heart attack and/or stroke, for example.
In view of these positive outcomes associated with Vitamin C, the general interest among the public is often how to maintain a lifestyle rich in Vitamin C intake.
Apart from supplements, one of the most reliable and robust sources of dietary Vitamin C are oranges.
In 2003 the American Journal of Nutrition (2003 Sep;78(3):454-60) concluded that taking 500ml of orange juice per day increased plasma concentrations of Vitamin C. Fresh-squeezed orange juice was used in the study with these results.
There are obviously other rich sources of Vitamin C (refer above) all of which, as and when accessible, should form part of any individual's dietary plan in order to prevent or reduce the risk of high blood pressure and heart disease in particular.
The conclusion is that the link between Vitamin C and heart disease has been scientifically proven to be of benefit one way or the other whether you believe in alternative medicine, mainstream science or both.
[Last updated: 04 January 2018]
|
Home > Vitamin C and Heart Disease |
Cardiovascular Definition > Vitamin C and Heart Disease |
Disclaimer
Information contained on this website is not meant to replace your doctor's advice.
(c) All Rights Reserved. 2010-2018